By: Endalkachew Mosisa Gutema 1, Mahesh Gopal 1 and Hirpa Gelgele Lemu 2
1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Engineering and Technology, Wollega University, Nekemte P.O. Box 395, Ethiopia
2 Department of Mechanical and Structural Engineering and Materials Science, Faculty of Science and Technology, University of Stavanger, N-4036 Stavanger, Norway
Abstract
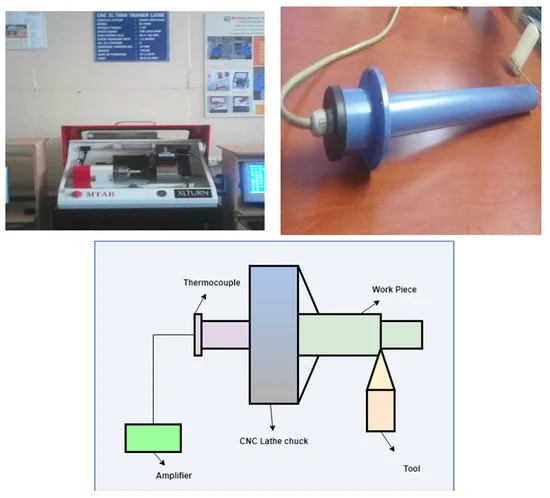
Because aluminium is a lightweight and low-density material, its alloys, such as Al 6061 alloy, are extensively used in numerous automobile, defense, and aviation components. This study aims to develop a predictive model to investigate the impact of tool nose radius on the CNC turning process of Al 6061 alloy and better recognize the implications of operating machining considering cutting speed, rate of feed, cutting depth, and tool nose radius. The trials were carried out by using the response surface methodology (RSM), with an Al2O3 coated carbide tool as the cutter and an Al 6061 workpiece as the material. A mathematical model of the second-order was created. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) approach was used to analyze the performance characteristics of the turning operation. Individual desirability values from the desirability function analysis for the multi-responses are used to construct a composite desirability value. The ideal parameter levels were determined by using the composite desirability value, and the significant impact of parameters was assessed by using the analysis of variance. The minimum temperature attained at the machining parameters are 98.0 m/min cutting speed, 0.26 mm/rev rate of feed, 0.893 mm cutting depth, and 0.84 mm tool nose radius. The best total desirability value is 23.615 °C, indicating that the experimental results are close to the predicted values. Download Full-Text![]()
Keywords: aluminium; cutting speed; response surface methodology; rate of feed; ANOVA; desirability function; cutting depth; tool nose radius